Online data storage has overtaken conventional storage in today’s business world. And one of the most important components of data storage is data encryption. Amazon’s S3, part of their AWS storage services, offers a number of different encryption methods. We’re going to look at what they provide, and which one is best suited for your business. We’re also going to run through the basics of data encryption, so that you can understand how best to secure your data.
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is a set of techniques used to ensure that stored data can only be viewed by authorised parties. Basic security measures include things like password protection. However, data encryption goes a step further. Data encryption uses algorithms to convert your stored data into coded data that can only be deciphered by a user with the correct password. This ensures that no unauthorised third parties can get to your data.
Encryption takes a number of different forms. The most basic of these is ‘at rest’ encryption. This simply means that stored data is encrypted so that only users with the correct password can view it. A more advanced form of encryption is end to end encryption. This refers to systems such as VPNs, where a package of data is encrypted at its source, put in transit, and then rendered readable. Within the Amazon S3 definition, encryption of data plays a major role.
Importance of Data Encryption
Encryption plays a key role in protecting sensitive information, especially if it’s stored in cloud environments like Amazon S3. That’s why encryption is essential for data security:
Protection of confidential information
Encryption protects sensitive data from unauthorized access. By converting readable data into an unreadable format, encryption protects the confidentiality of information even if it falls into the wrong hands.
Mitigating Data Breaches
Data breaches can have serious consequences. Encryption acts as a last line of security, ensuring that even if data is intercepted or accessed through hacking, it remains unintelligible and useless to an attacker.
Ensuring Data Integrity
Encryption not only protects data from unauthorized access, but also helps maintain its integrity.
Securing Data in Transit and at Rest
Data is vulnerable both when it is being transmitted across networks and when it is stored. Encryption provides comprehensive protection by securing data during transmission (data in transit) and while it is stored in the cloud (data at rest).
I am trying to make sure I have my S3 bucket secure. I need to allow some sort of public access due to my website displays the images that are uploaded to my S3 bucket. Any more suggestions on how to secure my S3 bucket? I basically just want user on my website to be able to view my images and upload images from only my site— from Stack Overflow
Amazon S3 Encryption Types
The Amazon S3 client makes use of two main encryption types, which we’re going to look at below. In addition, Amazon Elastic Block Store encryption is available, but the following two options are the main ones provided by default with S3:

SSE Data Encryption
SSE, or server side encryption, is the basic encryption method provided by S3. It ensures that all at-rest files are safely encrypted. There are two different options, which are mostly similar except for provision of the encryption code. The SSE-S3 option lets S3 choose an encryption code for you, which it uses to encrypt your files. The SSE-C option lets you choose your own code for encryption. In this case, S3 does not save your code, so you are responsible for keeping it secure.
S3 Client-Side Data Encryption
Client-side data encryption means that you as a user will be doing the encryption. Once you’ve used your own systems for encryption, the encrypted data is directly uploaded to AWS. You can then choose where you want your encryption keys stored. If you choose server-side, the keys will be uploaded to AWS, which will use its own management and storage systems to keep them secure. If you choose client-side, you’re responsible for storing your own keys. This is potentially more secure than storing them on AWS, though it means more work for you.
How to Configure AWS S3 Encryption?
Most AWS S3 encryption is done at the bucket level. This allows you to set encryption on a number of objects in a single bucket. You can also encrypt at an object level, which involves setting encryption for individual objects. However, generally speaking, you’re more likely to encrypt at bucket level. Encryption is done via the AWS console. Below, we’ll explain exactly how you go about encrypting at bucket level.
How to Encrypt an Amazon S3 Bucket
Encrypting an Amazon S3 bucket is easy. First of all, log in to the AWS console, and navigate to the bucket you want to encrypt. Click on the properties tab, next to the overview tab. From here, you can select the ‘default encryption’ option. You can now choose what kind of encryption you want to set on the bucket, such as server side or client side. Select your preference, and hit save. If you hit the change option, you’ll be able to check whether or not your encryption has been put in place on the bucket.
Solution for providing additional S3 encryption
You can boost your encryption and security by using CloudMounter. This program has been designed to mount Amazon S3, letting you map your entire Amazon cloud drive to your Mac. You can use your Mac’s search and browse functions to navigate through your cloud drive directly from your Mac. It offers client-side encryption, boosting security of all S3 files. On top of that, CloudMounter is compatible with a huge range of different cloud services, making it ideal for just about any user.
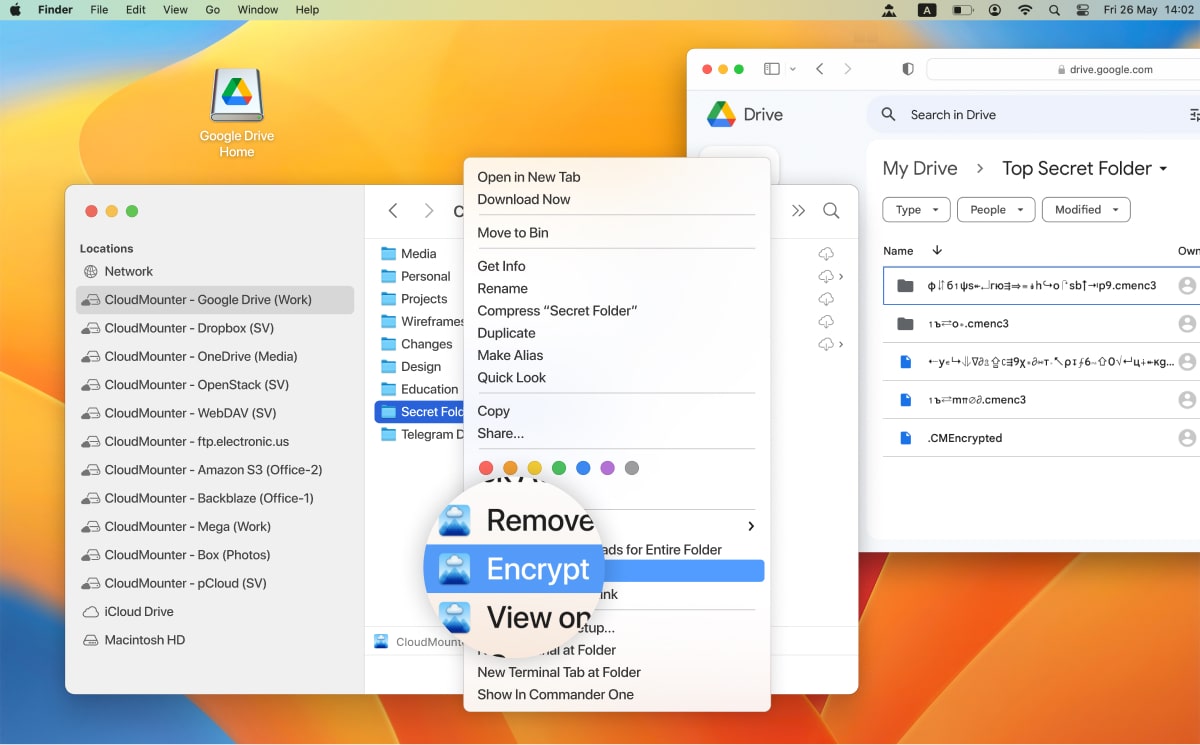
How to encrypt a directory with CloudMounter
1. Select the “Encrypt” option from the context menu.
Note: It is possible to encrypt the whole drive or any directory. Individual files cannot be encrypted.
2. Indicate a password and verify it. We also highly recommend to set a password hint to be able to recover it in future.
Note: CloudMounter doesn’t store any of your passwords. In case you lose/forget your password, it can’t be recovered. Your data will be irretrievably encrypted. Please, make sure you do not lose/forget it.
3. Tick the optional boxes, if you would like to add the password to the Keychain, additionally encrypt the names of the files or encrypt just newly added files.
To mask the encrypted files on your local machine, you will need to lock the encrypted directory by using the “Lock” context menu. You will be able to unravel these files later by using the “Unlock” option from the same context menu.
When the encryption is no longer needed, and you would like to decipher the directory, simply select the “Decrypt” option from the context menu, enter the password and confirm your actions.
Conclusion
Amazon S3 is a fantastic tool for data storage. And like most cloud drive storage systems available today, it does offer a certain level of security through encryption. However, anyone who wants the highest levels of guaranteed security should make use of CloudMounter. CloudMounter has been designed to provide you with solid encryption for a whole range of different storage types. As with all versatile security tools, it’s ideal for just about any user. And thanks to a range of easy to use features, it can do a lot more than just encryption. Check it out today.
Popular Articles
Frequently Asked Questions
AWS does not automatically encrypt data. However, as we’ve illustrated above, all you need to do is follow a few simple steps to set up encryption of all your saved files.
AES-256 AWS is Amazon’s standard server-side encryption. In other words, this is the default encryption it uses when instructed to encrypt data on the server-side, creating its own encryption code to keep your data safe.
Unless you have a program that encrypts data in transit, such as a VPN, your data is not automatically encrypted in transit. Various levels of security are available to encrypt data in transit, depending on your requirements.
The default encryption provided by AWS S3, such as AES-256, is completely free. If you want additional levels of security, you’re advised to invest in a third party solution such as CloudMounter.

