Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a cloud-based, long-term data storage. When Amazon calls S3 “simple storage”, it’s referring to the list of features provided by the service and definitely not the ease of use. To facilitate the work with S3 bucket and the files stored in the cloud, we recommend using CloudMounter – a reliable S3 client for your computer.
What is S3 bucket: understanding the term
Amazon platform doesn’t have a familiar file system. There is no such thing as a file or directory. The data stored and received through S3 are called objects. Each object is located inside a so-called bucket (a fundamental concept in S3), meaning a container for storing any number of objects.
S3 bucket name must be unique throughout the Amazon S3 system because it is an identifier for external access to bucket objects. Only you can access buckets, or you can allow others to do it. With the help of object attributes, you can allow or deny access to other people who want to download or upload files to your buckets.
How to create Amazon S3 bucket
If you already have an AWS account, you will be able to use Amazon S3 as this is the service that is with your Amazon account by default. In this article, we’ll show you how to create and customize an Amazon S3 bucket, upload files and folders, and configure properties and permissions.
1. Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
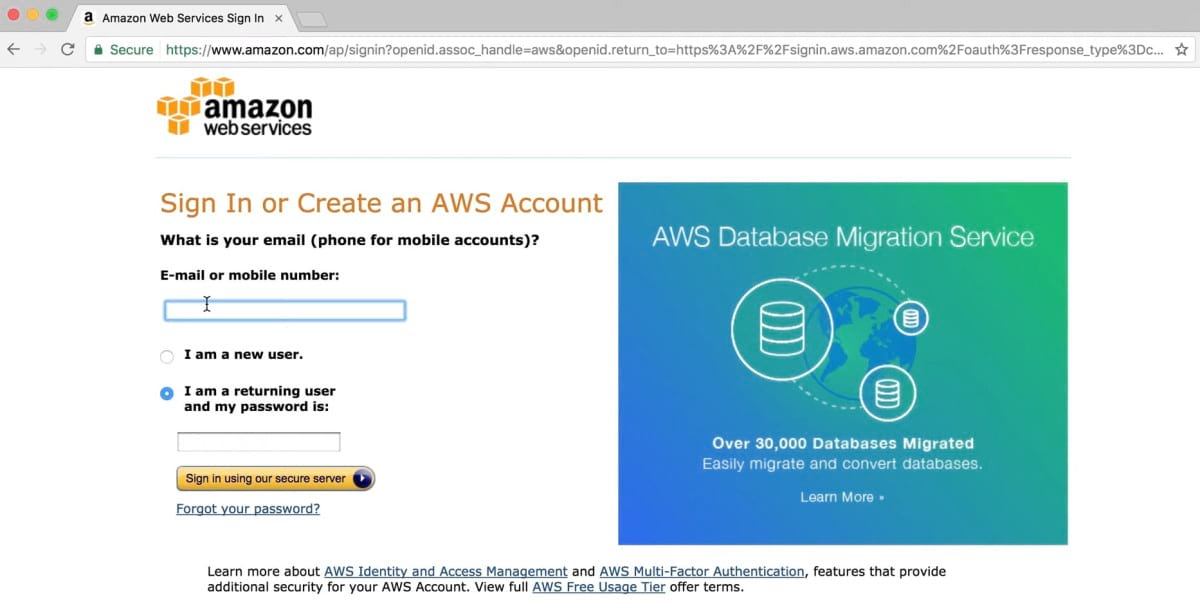
2. Click on the S3 service type in the search field. Click on S3 to access Amazon S3.
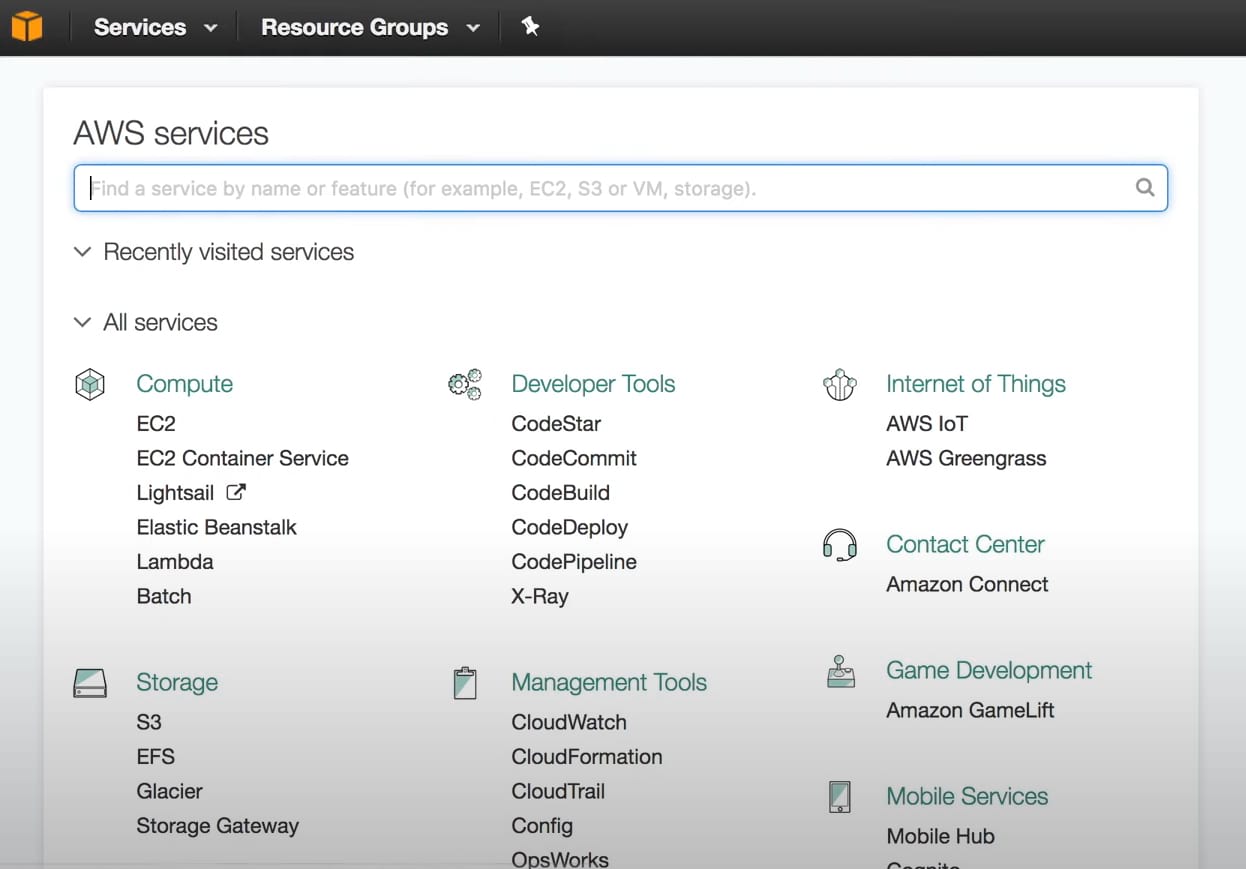
3. Click Create bucket, which will be used to upload items.
4. In the Name and Region field, enter S3 bucket name, select the Amazon region and click Next.
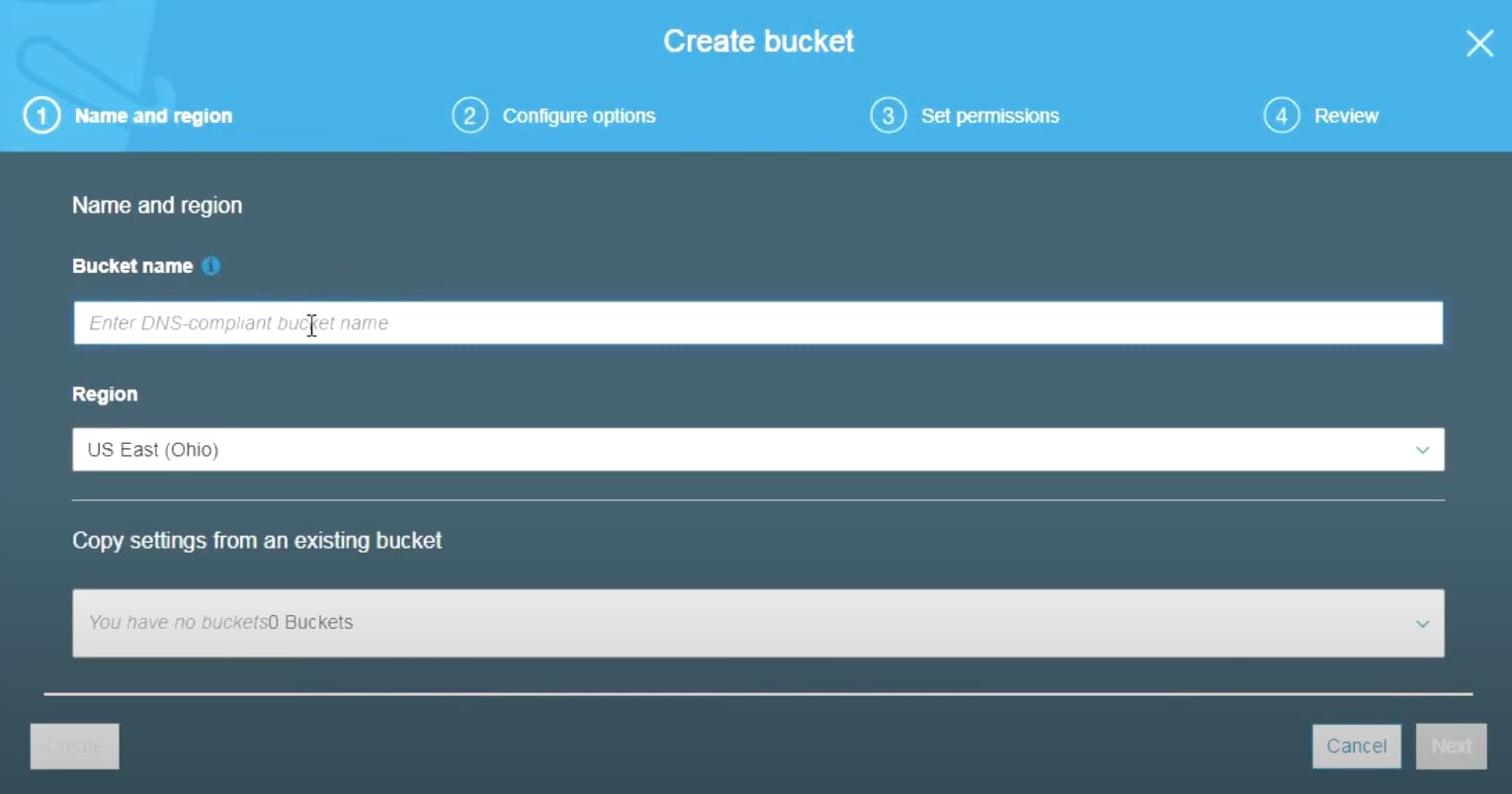
5. Under Configure Settings, configure your bucket and click Next.
6. In the Set Permissions section, configure the permission for AWS users who should (not) have access to the Amazon S3 bucket and click Next.
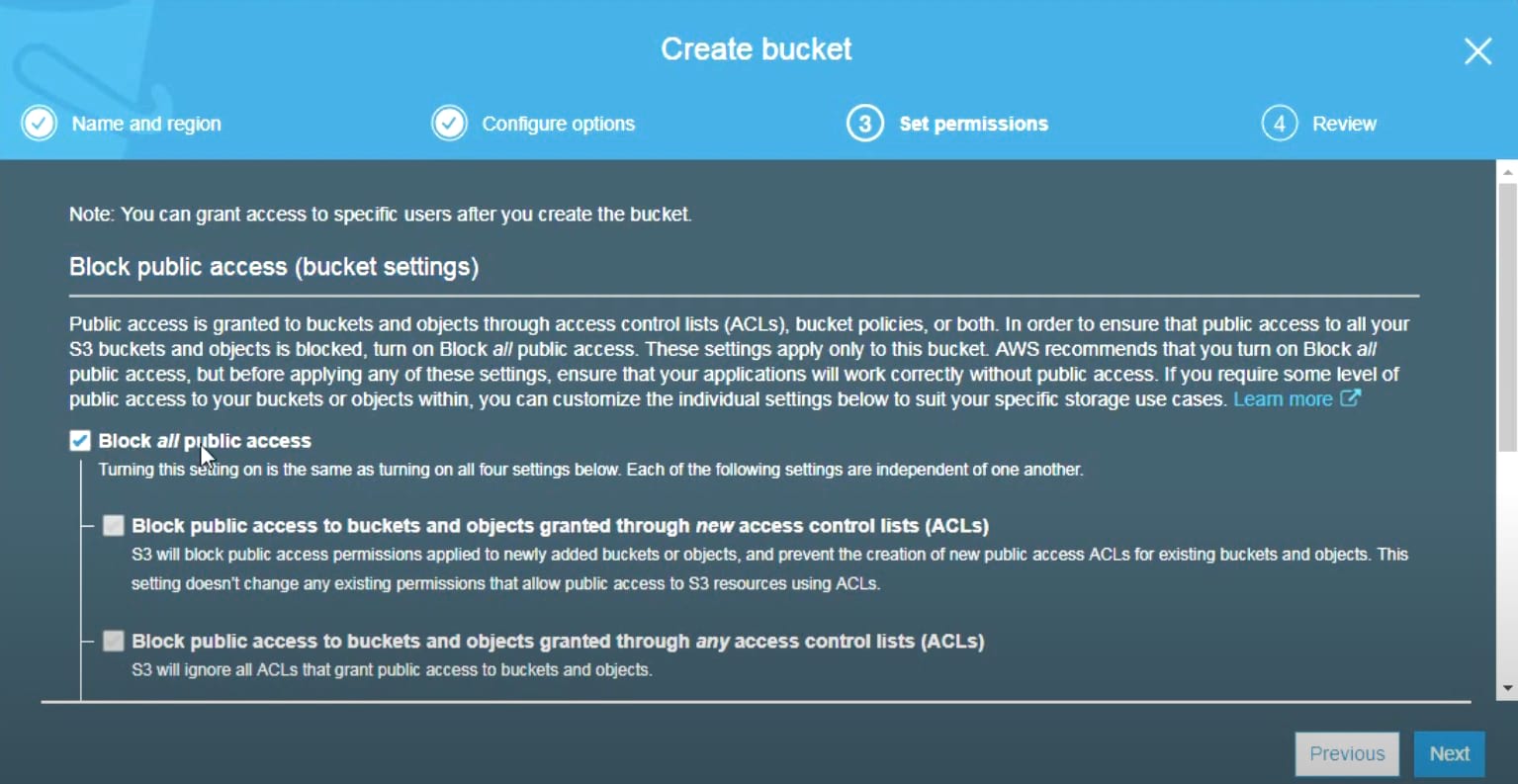
7. In the Check section, check if the configuration is correct and click Create bucket. Your Amazon S3 bucket is ready for use.
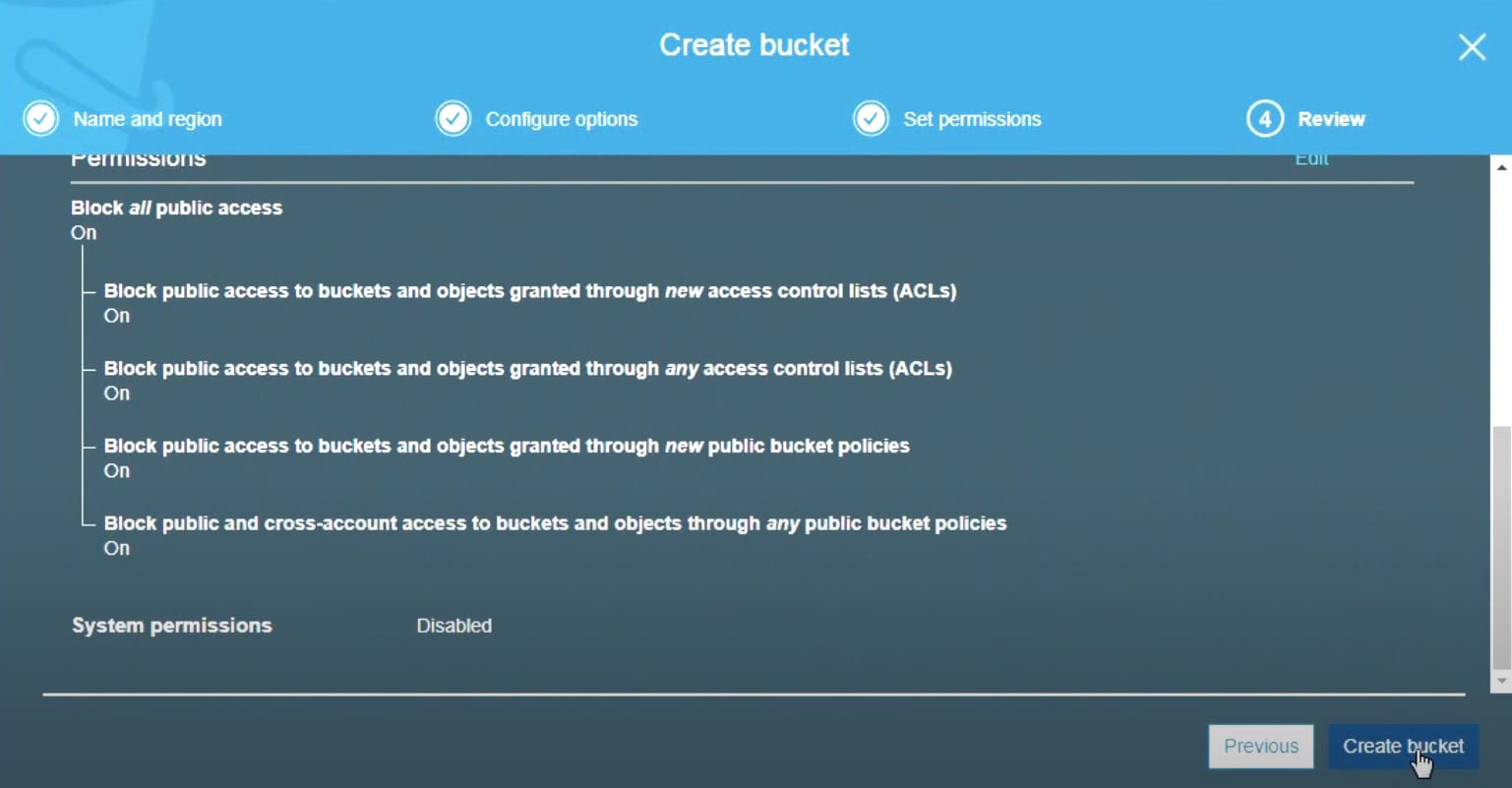
Please note that you cannot rename S3 bucket once it is created, as its name will be included in the URL.
The list of S3 bucket features
Amazon Web Services provides a wide set of features for Amazon S3 buckets. The list includes such things as:
- Version Control – allows you to store multiple versions of an object in one bucket. It can also be turned on whenever you want.
- Server Access Logging – provides detailed records for requests going into the S3 bucket and can be useful for security and access checks. However, logs will increase storage bills.
- Tags – allows to track bucket costs.
- Object-level logging – records object-level API actions using AWS CloudTrail at additional cost.
- Default Encryption – automatically encrypts objects as they are stored in Amazon S3. Data will be protected during transport (when it moves to and from the Amazon S3 bucket) and at rest (while it is stored on disks in Amazon S3).
- Advanced settings – permanently allow blocking of objects in this S3 bucket.
- Management – allows you to monitor requests in your bucket for an additional fee.
S3 bucket name: list of restrictions
There are several restrictions you should take into account when naming buckets. Keep in mind the following rules in order to avoid difficulties:
- Names can contain only lowercase letters, numbers, periods, underscores, and hyphens. The initial character of the name must be a letter or number.
- The name must not be in the style of an IP address (in other words, names like 10.0.0.1 are not allowed).
- The name must be at least 3 and no more than 63 characters long.
Amazon offers the following bucket naming conventions that will allow you to create valid and correct S3 bucket URL for your S3 objects:
- Do not create bucket names that include underscores (although this is officially allowed).
- Ideally, it is best to limit the length of a name to 63 characters.
- You should not create bucket names that end with a hyphen, and you should also avoid situations where the name is followed by a hyphen.
How to access Amazon S3 bucket
You can access Amazon buckets in several ways, namely via Amazon S3 console, via S3 bucket URL, and the last but not the least is via path-style or virtual-hosted-style. As you may have guessed, the third variant of accessing is for those users who are into coding and prefer doing everything programmatically whereas the first two are for regular users and are considered to be the most simple way.
Also, it is worth mentioning that sometimes bucket’s endpoint is called S3 URL because it’s location is displayed in a standard URL format and it can be found by following these steps:
- From the list of S3 buckets, click on the corresponding bucket name.
- Open the Properties tab.
- Choose the Static Website Hosting card. The first bit of information on the card is the endpoint address or S3 bucket URL.
S3 bucket limits and pricing
Amazon uses a regression scale: the more you host, the cheaper a gigabyte of storage costs. Besides that, you will have to pay separately for traffic, as well as requests to access objects ($ 0.01 per 1000 requests). To immediately understand how much you will be spending, you can use a special calculator.
By the way, you can create 10,000 S3 buckets for each of your accounts. This number can be increased to up to 1M at your request. As for the number of objects uploaded to S3 bucket, it is unlimited.
CloudMounter – an easy way to mount your S3 bucket
Unfortunately, without the help of third-party tools, you cannot mount S3 storage to your computer and deal with Amazon S3 buckets as with local folders. CloudMounter comes to the rescue here. You can choose whether to mount just one S3 bucket or several of them or even the entire Amazon Web Services account. Besides that, the app supports all AWS regions. In addition to being a perfect S3 client, the app works with a lot of other popular cloud computing services as well as remote servers.
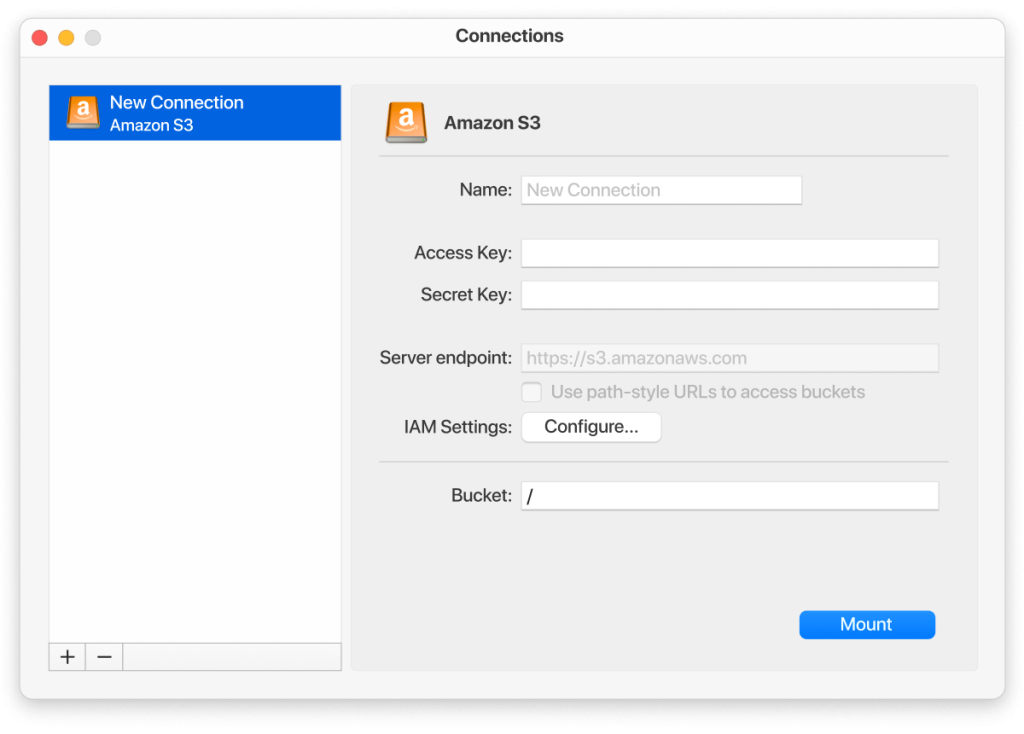
Working with Amazon Simple Storage Service via CloudMounter is very simple. You can upload files, download files, copy public and protected URL of your files. The only nuance is that it does not use a login/password for identification, but a pair of ID / private key, which you must obtain in the administration panel of Amazon services. Check this app and see what else it can offer you.
How to mount Amazon S3 on your computer
1. Install CloudMounter on your computer.
2. In an open app window select the Amazon S3 icon from the list.
3. Specify the name of the connection.
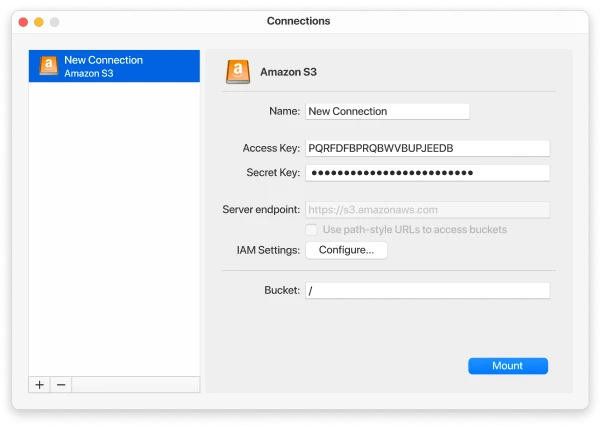
4. Enter the access key and secret access key.
5. Pick a style to use: path style or virtual-hosted style.
6. Enter the bucket name or specify the root directory using the slash character.
7. Click the Mount button. And now you can easily manage files between Amazon S3 and FTP, as an example.
Use Cases for S3 Storage
Amazon S3 is widely used for a variety of applications due to its flexibility, reliability, and scalability. Here are some common use cases for S3 storage:
- Backup and archiving. The S3 is often used for data backup and archiving. Its durability and high availability make it perfect for long-term storage of critical data.
- Data storage for web and mobile applications. S3 serves as back-end storage for web and mobile apps, providing scalable storage for user-generated content and application data.
- Big data and analytics. S3 is used to store large amounts of data that can be analyzed using big data tools and frameworks.
- Data sharing and collaboration. Using S3’s global network of edge points, content creators can share their files efficiently with end users, minimizing delays and enhancing the overall user experience.
Conclusion
As you see, all files are stored as an object in the Amazon S3 bucket. You can create multiple buckets; each bucket acts as a storage container. When you upload files to the bucket, you can set permission on the object and its data and determine who can access them. In addition, you can create AWS accounts in IAM, and determine who can create groups, upload or modify data.
Popular Articles
Frequently Asked Questions
Amazon S3 bucket is a container that stores objects. You can have an unlimited number of such buckets, and configure access for each of them.
The S3 model is built on a demand-driven basis – storage and data delivery are billed only when they are needed. What’s more, the security capabilities of S3 also let you specify when users can download a video and even specify who can download it.
Definitely not, S3 bucket is not a database, as it is a container where the objects are stored whereas Amazon S3 can be used as a database.
Yes, S3 buckets can have folders. You can delete, create new ones within one bucket. Unfortunately, you cannot rename a folder.